Fundamentals of Human Resource Management⁚ A Comprehensive Overview
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamentals of human resource management (HRM), a critical function within any organization. It delves into the core concepts, roles, and evolving trends of HRM, highlighting its strategic importance in achieving organizational success.
Introduction to Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a multifaceted and strategic function that plays a pivotal role in the success of any organization. It encompasses all aspects of managing an organization’s most valuable asset⁚ its people. From recruitment and selection to training and development, compensation and benefits, and employee relations, HRM encompasses a wide range of activities that contribute to the effective management of the workforce. HRM aims to align the organization’s human capital with its strategic objectives, ensuring that the right people are in the right place at the right time to achieve optimal performance.
In essence, HRM is about attracting, retaining, and developing a skilled and motivated workforce that can contribute to the organization’s overall success. It involves creating a positive and productive work environment, fostering employee engagement and satisfaction, and ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations. HRM is not merely an administrative function; it is a strategic partner in shaping the organization’s future and driving its competitive advantage.
The importance of HRM has grown significantly in recent years, driven by factors such as globalization, technological advancements, and the increasing focus on talent management. As organizations navigate a complex and dynamic business environment, HRM plays a critical role in supporting organizational growth, innovation, and adaptability. By understanding the fundamentals of HRM, individuals and organizations can effectively manage their human capital and unlock its full potential.
The Concept and Importance of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a strategic approach to managing an organization’s most valuable asset⁚ its people. It goes beyond simply managing administrative tasks and focuses on optimizing human capital to achieve organizational goals. HRM recognizes that employees are not just resources but key drivers of success, and it aims to create a positive and productive work environment that fosters employee engagement, satisfaction, and performance.
The importance of HRM lies in its ability to align human capital with the organization’s strategic objectives. By effectively managing recruitment, training, development, compensation, and employee relations, HRM ensures that the organization has the right people in the right roles, with the necessary skills and motivation to achieve its vision. In today’s competitive business environment, organizations that prioritize HRM gain a significant advantage by leveraging their human capital to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Moreover, effective HRM practices contribute to a positive and ethical work environment, fostering a sense of belonging and commitment among employees. By promoting diversity and inclusion, ensuring fair treatment and equal opportunities, and addressing ethical concerns, HRM helps create a workplace where employees feel valued and motivated to contribute their best. This, in turn, leads to higher employee retention, reduced turnover, and improved productivity, ultimately enhancing the organization’s overall performance and sustainability.
Functions and Role of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) encompasses a wide range of functions, all designed to optimize the organization’s human capital. These functions can be categorized into several key areas, each playing a vital role in attracting, developing, and retaining talent.
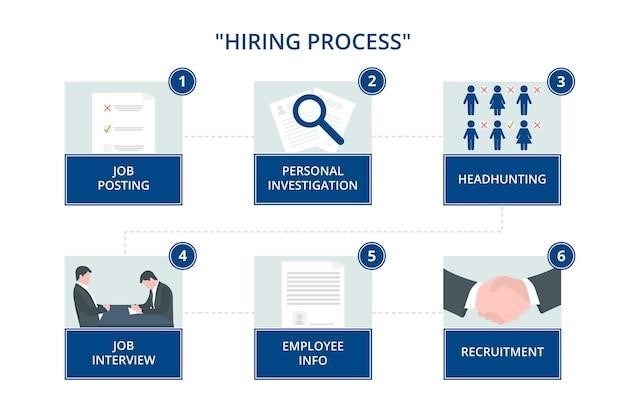
One of the primary functions of HRM is staffing, which involves identifying, attracting, and selecting qualified candidates to fill open positions within the organization. This includes activities such as job analysis, recruitment, interviewing, selection, and onboarding. Effective staffing ensures that the organization has the right people with the necessary skills and experience to perform their roles successfully.
Another crucial function is human resource development (HRD), which focuses on enhancing the skills, knowledge, and abilities of employees. This encompasses training and development programs, performance management systems, career planning, and succession planning. HRD aims to equip employees with the tools and opportunities they need to grow and contribute effectively to the organization’s success.
Other key functions include compensation and benefits, which involves determining and administering salary structures, benefits packages, and incentive programs. HRM also plays a vital role in employee relations, managing communication, resolving conflicts, and ensuring a positive and respectful work environment. These functions are interconnected, and their effective implementation is essential for building a strong and engaged workforce that drives organizational performance.
Globalization and its Impact on Human Resource Management
Globalization has profoundly reshaped the landscape of Human Resource Management (HRM), presenting both opportunities and challenges for organizations operating in a globalized world. The increasing interconnectedness of economies, markets, and cultures has led to a more diverse and complex workforce, requiring HRM professionals to adapt their strategies and practices to effectively manage this global talent pool.
One of the most significant impacts of globalization on HRM is the emergence of a global workforce, where organizations recruit and employ individuals from various countries and cultures. This necessitates the development of cross-cultural management skills to effectively communicate, collaborate, and lead diverse teams. HRM professionals need to be sensitive to cultural nuances, language differences, and work-life balance considerations in a global context.
Globalization also presents challenges related to legal and regulatory compliance, as organizations must navigate different labor laws, employment standards, and tax regulations in various countries. Furthermore, managing remote teams across different time zones and geographical locations requires advanced communication technologies and a clear understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities presented by virtual collaboration.
Changing Trends of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a dynamic field constantly evolving to adapt to changing societal, technological, and economic landscapes. Several significant trends are shaping the future of HRM, demanding that professionals embrace new approaches and skills to meet the evolving needs of organizations and employees.
One prominent trend is the rise of technology in HRM. Artificial Intelligence (AI), automation, and data analytics are transforming recruitment, training, performance management, and other HR functions. Organizations are increasingly adopting Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and gain valuable insights into workforce data.
Another significant trend is the growing emphasis on employee experience. Organizations are recognizing that attracting and retaining top talent requires creating a positive and engaging work environment that fosters employee well-being, development, and growth. This focus on employee experience includes promoting work-life balance, offering flexible work arrangements, and providing opportunities for professional development.
Ethical Issues in Human Resource Management
Ethical considerations are paramount in human resource management, as HR professionals are responsible for making decisions that impact the lives and well-being of employees. Ethical dilemmas can arise in various aspects of HRM, including recruitment, performance management, compensation, and employee relations. It is crucial for HR professionals to uphold ethical standards and principles in all their actions, ensuring fairness, equity, and respect for all individuals.
One significant ethical issue in HRM is discrimination. HR professionals must ensure that all recruitment and employment decisions are made based on merit and qualifications, free from bias based on race, gender, religion, sexual orientation, or other protected characteristics. It is essential to promote diversity and inclusion in the workplace, fostering a culture of respect and equality.
Another ethical challenge is maintaining employee privacy. HR professionals must handle employee information with sensitivity and confidentiality, ensuring that personal data is protected and used only for legitimate business purposes. They must also be mindful of the ethical implications of using technology to monitor employee activities, striking a balance between productivity and employee privacy.
The Strategic Role of Human Resource Management
Human resource management (HRM) has evolved from a purely administrative function to a strategic business partner, playing a crucial role in shaping an organization’s success. Rather than simply focusing on operational tasks like recruitment and payroll, modern HRM aligns its activities with the overall business strategy, ensuring that human capital contributes directly to organizational goals.
Strategic HRM involves actively identifying and developing talent that meets the organization’s needs, fostering a culture that promotes innovation and productivity, and ensuring that employees are motivated and engaged. HR professionals work closely with senior management to understand the organization’s vision and translate it into practical HR strategies, such as talent acquisition plans, training programs, performance management systems, and compensation and benefits packages.
By adopting a strategic approach, HR can contribute significantly to organizational growth and competitiveness. It can help attract and retain top talent, improve employee performance, enhance organizational culture, and create a positive work environment that drives innovation and business success. In today’s dynamic business landscape, strategic HRM is essential for organizations to thrive and achieve their long-term objectives.
Human Resource Management as a Profession
Human resource management (HRM) has evolved into a dynamic and multifaceted profession, attracting individuals passionate about people management and organizational development. The field offers diverse career trajectories, from generalist roles to specialized areas like talent acquisition, compensation and benefits, training and development, and employee relations.
The profession demands a blend of skills, including strong communication and interpersonal abilities, analytical thinking, problem-solving, and a deep understanding of labor laws and ethical principles. HR professionals must be adept at navigating complex organizational dynamics, fostering positive employee relations, and contributing to a culture of inclusivity and respect.
To enhance their professional credibility and stay ahead of the curve, HR professionals often pursue certifications from reputable organizations like the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) or the Chartered Institute of Personnel Development (CIPD). These certifications demonstrate competence, knowledge, and commitment to the profession, opening doors to leadership opportunities and career advancement.
Human Resource Management Systems
Human resource management systems (HRMS) are software applications designed to streamline and automate various HR processes, enhancing efficiency and data management within organizations. These systems typically encompass modules for recruitment, onboarding, payroll, performance management, talent development, and employee benefits administration.
HRMS solutions offer a centralized platform for managing employee data, simplifying administrative tasks, and providing real-time insights into workforce performance. They enable organizations to track key metrics, identify talent gaps, and make data-driven decisions regarding employee engagement, training, and compensation.
The adoption of HRMS has become increasingly prevalent across industries, as organizations recognize the value of technology in managing their human capital effectively. Cloud-based HRMS solutions are particularly popular, offering flexibility, scalability, and reduced infrastructure costs.

The Future of Human Resource Management
The future of human resource management (HRM) is shaped by rapid technological advancements, evolving workforce demographics, and a growing emphasis on employee experience. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and automation are transforming traditional HR processes, enabling data-driven decision-making and personalized employee experiences.
The rise of remote work and flexible work arrangements is reshaping the workplace landscape, requiring HR professionals to adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Furthermore, the increasing diversity and inclusion initiatives are driving a focus on creating equitable and inclusive work environments that attract and retain a diverse workforce.
As the world of work continues to evolve, HR professionals will need to embrace a strategic mindset, develop data-driven insights, and cultivate strong communication and interpersonal skills to navigate the future of HRM effectively.
In conclusion, human resource management (HRM) plays a pivotal role in the success of any organization. Understanding the fundamental principles of HRM, encompassing its functions, importance, and evolving trends, is essential for effective people management. As the workplace landscape continues to evolve, HR professionals must adapt and embrace a strategic mindset, focusing on talent acquisition, development, engagement, and retention.
By leveraging technology, fostering a culture of diversity and inclusion, and prioritizing employee well-being, organizations can create a positive and productive work environment that attracts and retains top talent. Ultimately, effective HRM practices contribute to organizational growth, competitiveness, and long-term sustainability.